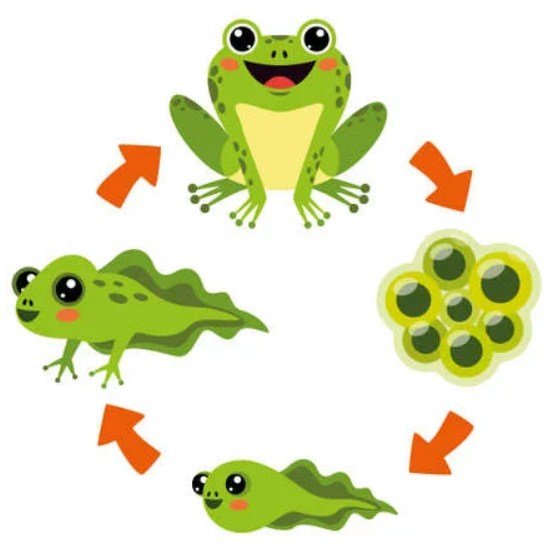
Frogs are fascinating creatures that come in several colors, sizes, and shapes. They belong to the class Amphibia and undergo a unique transformation during their lifecycle. They start as eggs, then hatch into tadpoles, grow into juveniles, and eventually, they become adult frogs.
With the help of a frog clipart, you can have a peek into their remarkable lifecycle and learn more about their different stages. In this article, we will go through each stage in detail, from the egg to the adult, and understand how a frog clipart can bring this incredible process to life.
The Egg Stage
The first stage of a frog’s lifecycle starts with the egg. Frogs lay their eggs in clusters in the water or moist environments like leaves and branches. The egg is usually spherical and transparent and contains a yolk that supplies the needed nutrients for the embryo. The egg stage lasts for about one to three weeks, depending on the species and environmental conditions. Here are some interesting facts about frog eggs:
- Frog eggs are delicate and need to be protected from predators like fish, birds, and insects.
- Some frog species lay their eggs in foam nests called ‘rafts.’
- The temperature of the water determines the hatching time for frog eggs.
The Tadpole Stage
After the eggs hatch, they become tadpoles, which are baby frogs that look like fish. The tadpole stage lasts for several weeks to months, depending on the species. During this stage, tadpoles live in the water and breathe through gills. Here are some unique characteristics of tadpoles:
- Tadpoles have a long, cylindrical body with a flat tail that they use to swim.
- Their diet consists of algae, plants, and small aquatic animals.
- As they grow, tadpoles develop hind legs first before their front legs.
The Juvenile Stage
After completing the tadpole stage, the frog enters the juvenile stage. In this stage, the frog develops lungs and leaves the water to live on land. The juvenile frog is small and has a slim body with long hind legs, which allows it to jump great distances. Here are some interesting facts about juvenile frogs:
- Juvenile frogs have a voracious appetite and feed on insects and small invertebrates.
- They can live in moist areas that provide cover and protection.
- Juvenile frogs are vulnerable to predators like birds, snakes, and small mammals.
The Adult Stage
The adult stage is the last and most recognizable stage in a frog’s lifecycle. At this stage, the frog develops into its final size and shape and is fully adapted to life on land. Adult frogs can live up to several years in their natural environment. Here are some exciting characteristics of adult frogs:
- Adult frogs have a wide range of colors and patterns to help them blend into their surroundings.
- They have long, sticky tongues that they use to catch prey.
- Their diet consists of insects, small animals, and even other frogs.
Importance of Frog Clipart
Frog clipart is essential in understanding a frog’s lifecycle because it helps visualize each stage through illustrations. Frog clipart can also be used in educational materials, especially for kids, to make learning more fun and interactive. Here are some advantages of using frog clipart:
- Frog clipart makes learning about frog life cycle more engaging and memorable.
- It helps teachers and parents explain complex biological concepts easily.
- Frog clipart can be used in various materials such as textbooks, presentations, and children’s books.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the life cycle of a frog clipart is both exciting and educational. By visualizing each stage in the frog’s lifecycle, we can understand their incredible transformation from egg to adult. Frog clipart can also play a vital role in teaching kids about these fascinating creatures while making learning more enjoyable. No matter how old you are, frog clipart can be a fun way to explore and learn about the world around us.
FAQ
1. What is the average lifespan of a frog?
The average lifespan of a frog varies depending on the species, but it can range from a few years to over a decade in the wild.
2. What kind of predators do frog eggs face?
Frog eggs are vulnerable to predators like fish, birds, and insects. Some frog species lay their eggs in foam nests called ‘rafts’ to protect them from predators.
3. How do tadpoles breathe underwater?
Tadpoles breathe through gills, which are located on the sides of their body. As they grow, they develop lungs and eventually leave the water to live on land.
4. What kind of environment do juvenile frogs prefer?
Juvenile frogs prefer moist areas that provide cover and protection, such as near streams, ponds, or other bodies of water.
5. How do adult frogs catch their prey?
Adult frogs have long, sticky tongues that they use to catch their prey. They usually feed on insects, small animals, and even other frogs.
