As someone with extensive experience in the world of computer hardware, I understand how crucial it is to have the right components for optimal performance. One such component is the NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) storage device, which has become increasingly popular due to its speed and efficiency. In this article, I will guide you through the process of determining whether your motherboard supports NVMe or not.
So, does your motherboard support NVMe? The answer depends on your motherboard’s specifications, particularly the presence of an M.2 slot and compatibility with the NVMe protocol. To find out, you’ll need to examine your motherboard’s documentation or check its BIOS/UEFI settings. By following the steps outlined in this article, you’ll be able to determine if your system can take advantage of the benefits offered by NVMe storage devices. So, let’s dive in and explore this topic further!
What is NVMe and Why is it Important?
NVMe, or Non-Volatile Memory Express, is a high-performance storage protocol designed specifically for NAND flash memory-based SSDs (Solid State Drives). It was developed to overcome the limitations of older storage interfaces like SATA and provide faster data transfer speeds. NVMe operates directly through the PCI Express (PCIe) bus, which allows for much higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to traditional storage protocols.
As the demand for faster storage devices has increased, NVMe has emerged as the go-to solution for many users. This is because NVMe SSDs offer significantly improved performance compared to their SATA counterparts, with data transfer speeds up to six times faster. The reduced latency of NVMe drives also leads to faster system boot times, quicker application launches, and overall improved system responsiveness.
According to a recent market research report, the global NVMe market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 28.0% from 2021 to 2026, reaching a value of $44.2 billion by 2026. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for high-speed data storage solutions in various industries, including gaming, data centers, and professional workstations. As a result, understanding whether your motherboard supports NVMe is crucial if you want to take advantage of these performance benefits and stay ahead of the curve.
Identifying Your Motherboard’s Specifications
Before you can determine whether your motherboard supports NVMe, you need to identify its specifications. This includes information about the type of chipset it uses, the presence of M.2 slots, and compatibility with the NVMe protocol. Knowing these details will help you understand if your system is capable of using an NVMe SSD or if you need to consider upgrading your motherboard.
You can find your motherboard’s specifications in several ways:
- Refer to the user manual or product documentation that came with your motherboard.
- Visit the manufacturer’s website and search for your specific motherboard model.
- Use software tools like CPU-Z, HWiNFO, or Speccy to gather information about your system’s hardware components.
Once you have identified your motherboard’s specifications, you can proceed to check if it supports NVMe by examining its M.2 slots and compatibility with the NVMe protocol.
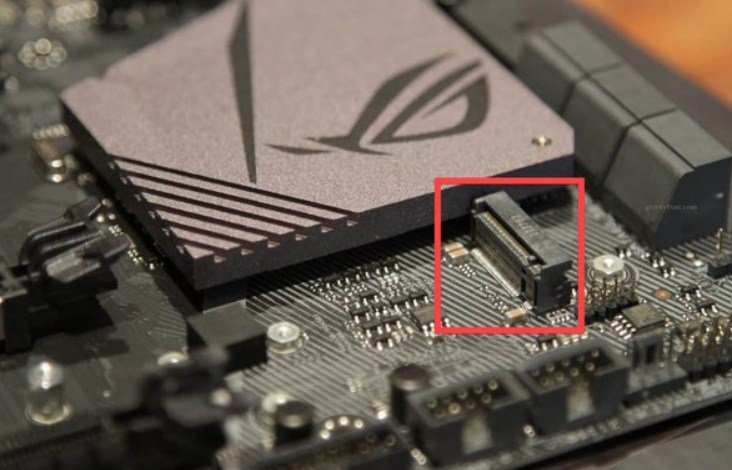
How to Check for NVMe Support in BIOS/UEFI
After identifying your motherboard’s specifications, the next step is to check if it supports NVMe through its BIOS or UEFI settings. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) are firmware interfaces that manage the communication between your system’s hardware components and the operating system. By accessing these settings, you can verify if your system is compatible with NVMe storage devices.
To check for NVMe support in BIOS/UEFI, follow these steps:
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI setup by pressing the appropriate key (usually F2, F10, DEL, or ESC) during the boot process. The exact key may vary depending on your motherboard’s manufacturer, so consult your user manual if needed.
- Once inside the BIOS/UEFI settings, navigate to the “Storage” or “Advanced” section.
- Look for an option related to “NVMe Configuration” or “M.2 Configuration.” If present, this indicates that your motherboard supports NVMe storage devices.
- Additionally, check if there is an option to enable or disable NVMe support. Ensure that it is enabled to take advantage of the performance benefits offered by NVMe SSDs.
If you do not find any options related to NVMe in your BIOS/UEFI settings, it is likely that your motherboard does not support NVMe storage devices. In this case, you may need to consider upgrading your motherboard or explore alternative storage solutions.
Pros and Cons of Using NVMe SSDs
NVMe SSDs have become increasingly popular due to their high-speed performance and efficiency. However, like any technology, they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the pros and cons of using NVMe SSDs will help you make an informed decision when considering whether to upgrade your storage system.
Some of the key advantages of using NVMe SSDs include:
- Faster data transfer speeds: NVMe SSDs can achieve significantly higher read and write speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs, resulting in improved overall system performance.
- Lower latency: NVMe drives provide lower latency, which translates to faster boot times, quicker application launches, and more responsive systems.
- Scalability: NVMe SSDs are designed to work seamlessly with the PCIe interface, allowing for easy scalability as your storage needs increase.
- Energy efficiency: Compared to SATA SSDs, NVMe drives consume less power, making them more energy-efficient and suitable for use in laptops or other portable devices.
On the other hand, there are some disadvantages to using NVMe SSDs:
- Higher cost: NVMe SSDs tend to be more expensive than their SATA counterparts, which may be a concern for budget-conscious users.
- Compatibility issues: Not all motherboards support NVMe, meaning you may need to upgrade your motherboard or explore alternative storage solutions if you want to use an NVMe drive.
- Limited availability: While the market for NVMe SSDs is growing rapidly, they are still not as widely available as SATA drives, particularly in lower-capacity options.
Despite these drawbacks, the benefits of NVMe SSDs often outweigh the disadvantages, particularly for users who prioritize speed and performance in their systems.
Upgrading Your Motherboard for NVMe Compatibility
If your current motherboard does not support NVMe, you may want to consider upgrading it to take advantage of the performance benefits offered by NVMe SSDs. Upgrading your motherboard involves selecting a new board that is compatible with your system’s other components, such as the CPU, RAM, and GPU. Additionally, the new motherboard should have an M.2 slot and support the NVMe protocol.
When selecting a new motherboard for NVMe compatibility, keep the following factors in mind:
- Form factor: Choose a motherboard with the same form factor as your current one (ATX, Micro-ATX, or Mini-ITX) to ensure it fits inside your computer case.
- CPU socket: Make sure the new motherboard has the same CPU socket type as your current processor to avoid compatibility issues.
- RAM slots: Consider the number of RAM slots available on the new motherboard and whether it supports the same RAM type as your existing memory modules.
- Expansion slots: Check the number of PCIe slots available on the new motherboard, as well as their sizes and speeds, to accommodate your GPU and other expansion cards.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a suitable motherboard that will allow you to enjoy the benefits of NVMe storage devices while maintaining compatibility with your existing hardware components.
Conclusion: To Wrap Up
In conclusion, NVMe SSDs offer significant performance improvements over traditional SATA SSDs, making them an attractive storage solution for those seeking faster data transfer speeds and lower latency. By understanding your motherboard’s specifications, checking for NVMe compatibility in BIOS/UEFI, and considering the pros and cons of using NVMe SSDs, you can make an informed decision about whether to upgrade your storage system. With the right knowledge and tools, you can harness the power of NVMe technology to enhance your computing experience and put a smile on your face.
FAQ
- What is NVMe? NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-performance storage protocol designed specifically for NAND flash memory-based SSDs (Solid State Drives). It offers faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
- How do I know if my motherboard supports NVMe? You can check your motherboard’s specifications by referring to its user manual or product documentation, visiting the manufacturer’s website, or using software tools like CPU-Z, HWiNFO, or Speccy.
- How can I check for NVMe support in BIOS/UEFI? Enter your system’s BIOS/UEFI settings during the boot process and look for options related to “NVMe Configuration” or “M.2 Configuration.” If present, this indicates that your motherboard supports NVMe storage devices.
- What are the advantages of using NVMe SSDs? NVMe SSDs offer faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, improved scalability, and better energy efficiency compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
- What are the disadvantages of using NVMe SSDs? Some disadvantages of NVMe SSDs include higher cost, compatibility issues with older motherboards, and limited availability in comparison to SATA SSDs.
- How can I troubleshoot NVMe issues on my motherboard? Troubleshooting NVMe issues may involve checking the BIOS settings, updating firmware and drivers, ensuring compatibility with the motherboard, and using diagnostic tools to monitor drive health.
- Do I need to upgrade my motherboard for NVMe compatibility? If your current motherboard does not support NVMe, you may need to upgrade it to take advantage of the performance benefits offered by NVMe SSDs. Ensure that the new motherboard has an M.2 slot and supports the NVMe protocol.
